In which case to make a URL redirection ? What are the different existing redirects (300, 301, 304, etc.) and which one to apply depending on your situation? Answer in this article.
What is a URL redirect?
A URL redirection is a mechanism that automatically sends an Internet user (and search engines) from one web address to another. It is used when a page has changed address, been deleted or merged with another. For example, if you move a blog post, the redirection prevents visitors from landing on an error page (404). In SEO, it is an essential practice to preserve SEO and transfer authority from the old page to the new one. The most common redirects are 301 (permanent) and 302 (temporary), depending on whether the change of address is permanent or not.
Although this practice is very useful, it sometimes remains complex to carry out. There are in fact several types of URL redirection and you should choose the right one, the one adapted to your situation, so as not to degrade the user experience or your natural referencing.
What are the different URL redirections that exist?
There are several types of URL redirects, each having a specific function depending on the context and the desired objective. Here they are:
- The 301 redirect (permanent) indicates that the page has been permanently moved to a new address. It almost entirely transfers the SEO value from the old page to the new one and should be used when making a permanent URL change.
- The 302 redirect (temporary) signals that the move is only temporary — useful, for example, when redesigning or testing a page.
- The 307 redirectmore recent, replaces 302 in modern protocols (HTTP/1.1) and retains the request methods.
- Meta refresh redirection, executed on the browser side after a few seconds, but not recommended for SEO.
- Canonical tag : is not a redirect strictly speaking, but it tells search engines which version of a page should be considered the main one to avoid duplicate content.
When to use a URL redirect?
A URL redirect can be used in many situations that you will certainly face one day. Among the most common, we can cite the following.
Domain name change
When your domain name is too long or is no longer representative of your activity, you are often forced to change it.
A URL redirection is necessary to redirect people who come across your old site to your new site.
Access to the same web page via different URLs
When the same content is accessible via different URLs, this creates duplicate contentwhich is very bad for your natural referencing. This is often the case for the home page of a site.
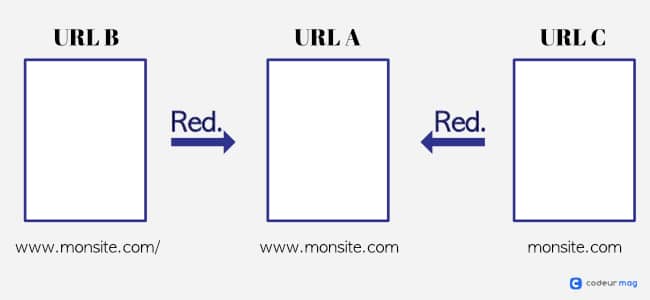

Let's say that your home page can be visited via three URLs: URL A, URL B and URL C. With a redirect, for example, you can redirect all users who arrive at URLs B and C to URL A. This tells Google which page should be indexed and gives it more authority.
Editing URLs
Editing URLs can be useful when you're updating your site and changing your URL structure. Let's take the example of an e-commerce site: your product entitled “cup of tea” is accessible via the following URL: www.monsite.com/categorie/dishes/tasse-de-the.
If you decide to remove the “category” directory to simplify and reduce the length of your URLs, your product will then be accessible via www.monsite.com/dishes/tasse-de-the.
If you don't create a redirect, it's likely that people will encounter a 404 error when clicking on the old URL. This can happen if a third party site has linked your product before the change made to your URLs.
Access to a multilingual site
If you operate internationally and have your site in different languagesyou can create URL redirects. These make it possible to display to Internet users the correct version of the content according to their geographical position.
URL redirections can also be implemented if you merge two websites, if you delete a web page or if you no longer want to use “www” (or vice versa).
The main types of URL redirection
There are two types of URL redirection:
- Client-side redirection;
- Server-side redirection.
The latter is executed by a server as its name indicates, while the first is carried out directly by the “client”, very often the user's browser.
Server-side redirects
Server-side redirects are the most common. For an Internet user to be redirected to a URL, an HTTP request is made to the web server. The latter then delivers an HTTP status code which specifies the redirection to be carried out.
The status code corresponds to the name of the redirects. These can be temporary or permanent.
| HTTP status code | Redirect | Temporary or permanent |
| 301 | 301 redirect | Permanent |
| 302 | 302 redirect | Temporary |
| 307 | 307 redirect | Temporary |
Client-side redirects
If these redirects are used less, it is mainly because they have several disadvantages in terms of SEO. To name just one, search engines don't always notice client-side redirects and when this happens, the authority of the old web page is not transferred to the new one.
However, it is good to know the two types of client-side redirection:
- The Meta refresh : it automatically redirects the user to another URL after a delay, such as after an online payment;
- JavaScript redirection : it asks the browser, via JavaScript code, to load another URL
Which URL redirection to choose?
There are several types of redirects. Find out which type of redirection to choose based on the different situations you may encounter.
The 301 redirect
This is certainly the most used URL redirection to redirect pages. You need to set it up if you want to permanently redirect users who arrive on a page that has been deleted or moved, or for which the permalink structure has been modified.
The 301 code tells Google several things:
- The page in question is no longer available at this URL;
- The page should no longer be indexed;
- The link juice from the old page should be transferred to the new one.
You therefore understand that a 301 redirect allows you to retain the authority of your old page.
Warning: Before setting up such a redirection, make sure that your old URL will no longer be used, as it will be difficult to go back.
To set up a redirection between two pages, open your .htaccess file and insert the following code:
Redirect 301 /ancienne-page https://example.com/nouvelle-pageAnother solution, you can insert into the HTML source code of the page to be redirected (section
) the following PHP code:
header("Location: https://example.com/nouvelle-page", true, 301);
exit();For more complex cases, call a qualified freelance developer. Editing the .htaccess file should not be taken lightly. Indeed, in the event of an error, it can cause significant damage to your site.
Concerning WordPress, free plugins exist to redirect pages.
The 302 redirect
This temporary redirect indicates that the content was found, but is currently located at a different URL. You can therefore temporarily redirect visitors to this other web page.
The 302 redirect originally did not involve any transfer of authority, which is why it is so rarely used. But today, the situation seems to have changed.
You can use it when content from URL A has been temporarily moved to URL B, or when you want to redirect your visitors to the correct language version of your site.
As with the 301 redirect, you can perform a 302 redirect via the source code of the page to be redirected or directly from the .htaccess file. In the first case, insert the following PHP code:
header("Location: https://example.com/nouvelle-page", true, 302);
exit();You can also modify the .htaccess file to make a 302 redirect between two pages:
Redirect 302 /ancienne-page https://example.com/nouvelle-pageThe 307 redirect
While the 302 redirect is more complex, the 307 redirect clearly indicates that an A URL has been moved for a short time. This redirection is to be used if your site is under maintenance for example.
Since this is a temporary redirect, search engines do not take into account the authority of the old URL.
As for the 302 redirect, you can indicate it in PHP:
header("Location: https://example.com/nouvelle-page", true, 307);
exit();or by modifying the .htacess file:
Redirect 307 /ancienne-page https://example.com/nouvelle-pageRedirects should be used in specific cases and sparingly. So that they are relevant and do not have a negative impact on your SEO, take the time to analyze your situation to choose the right redirection to carry out.
How to easily create a URL redirection on WordPress?
On WordPress, there are several ways to create a URL redirect to avoid 404 errors and preserve SEO. The easiest method is to use a dedicated plugin, like Redirection or Yoast SEO Premium, which make it easy to set up 301 or 302 redirects without touching the code.
For more advanced users, it is also possible to create a redirect directly via the .htaccess file (for Apache servers) or via the rewrite rules on Nginx, by adding the corresponding line to the source URL and the target URL. Finally, WordPress also offers the native “Redirect URL” function in certain themes or SEO extensions, allowing you to redirect a page or article to a new address quickly and easily.
If you prefer to entrust this task to an expert, do not hesitate to call on a WordPress developer. This professional will know how to configure your redirections properly, optimize your performance and avoid any technical errors that could impact your SEO.
